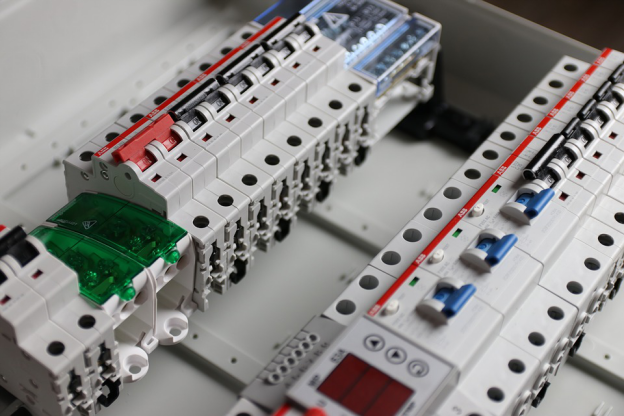
The History of Circuit Breakers and Fuses
Thomas Edison patented both a circuit breaker and fuse. Edison patented the circuit breaker design in 1879, and Edison patented a fuse for his electrical distribution system in 1890. Over one hundred years later, both fuses and circuit breakers are still used to protect electrical wiring and equipment from damage due to power outages, surges, and overloads.
So to cut to the chase, what’s better, a fuse box or circuit breaker?
The answer to this question varies on a case-to-case basis and depending on who you ask. The answer is controversial for some electricians, and you usually won’t get the same answer depending on what electrician you ask.
The rest of this blog post will explore both sides and take a closer look at the benefits and downsides of fuses versus circuit breakers. Unfortunately, we can only share the facts and definitions of each, but in the end, you have to decide what’s best for your home.
For advice from a local Massachusetts-based electrician call Integrity Electrical Services at (978) 753-8350. Without further ado, let’s dive in!
What is a Circuit Breaker?
A circuit breaker is supposed to be an improved version of a fuse box. The circuit breakers are those black switches that you can switch on and off inside your panel box.
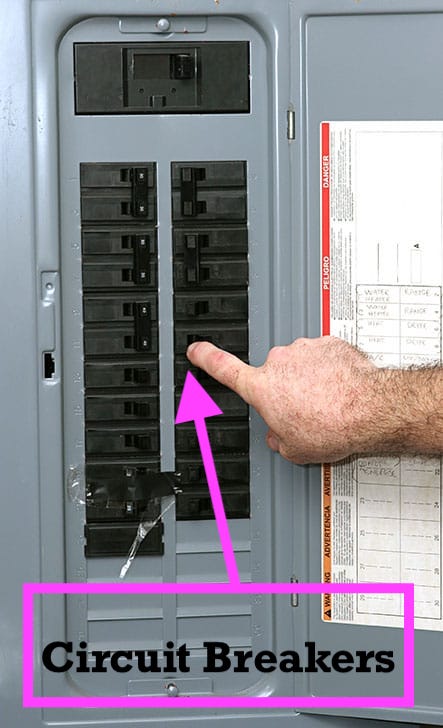
Inside each circuit breaker resides a wire which carries the electricity into a little thermomagnetic device and then out to the wire itself. The thermomagnetic device inside the circuit breaker distorts when the wire heats up, similar to the little metal strip inside a fuse (which we’ll explain).
When electricity heats up beyond its standard capacity, that thermomagnetic device distorts and shuts the electricity off immediately to fix the overload. The thermomagnetic device continues measuring the heat instead of destroying itself as a fuse would do. So you can then flip the circuit breaker back on, and no need to replace it.
If your electricity goes out briefly during a storm, you may only need to open your electrical panel box and turn back on all the circuit breakers. This is because circuit breakers are resettable, unlike fuses that get thrown out after each usage. We’ll talk more about this subject below.
What is a Fuse Box?
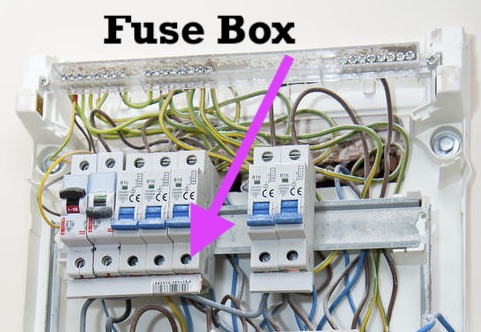
A fuse is a simple device used to protect circuit wires from overheating and causing a fire. Fuses live in a fuse box.
How a Fuse Works:
Fuses and circuit breakers work in symphony with your electrical panel. Your electrical panel is what takes in power from your utility company and then distributes the power to various circuits throughout your home.
Electricity flows through your house through wires. The Smaller the wire, the less electricity. The bigger the wire, the more electricity it carries. If any wire takes in too much electricity at once (i.e., the current), it can heat up and cause a fire. The current is measured in amps, like 15, 20, and 30 amp.
Circuit breakers and fuses come into play if there’s an overload, potentially resulting in a fire, where the fuses or circuits shut off the power. For example, with a fuse, the metallic strip inside the fuse melts faster than the wire if there’s an overflow of current, immediately shutting off the electricity for that wire.
What’s the purpose of a circuit breaker and fuse box?
Fuse boxes and circuit breakers serve the same purpose: to prevent overloads and protect the electrical circuits.
So our residential electricians are constantly being asked what’s better, using a fuse box or circuit breaker. Especially when it comes to new construction in MA, homeowners want to build their homes with the best quality material and always include the latest technology, so the question often is; Should we use a fuse box or circuit breaker.
Fuse Box Vs. Circuit Breakers – What’s better?
Most older homes use a fuse panel. However, newer modern homes will usually have circuit breakers. In addition, as of 2021 and beyond, many residential properties are investing in EV chargers, standby generators, and utilizing lots of new technology, resulting in many homes in Massachusetts requiring at least a 200 amp circuit breaker panel.
In fact, in Massachusetts, many homes will be upgraded to 300-400 amp circuit breaker panels due to the Biden Administration’s policies. But the good news is, by upgrading your circuit breaker panel, you’re simultaneously increasing the value of your property, so it’s a win-win!
Do Circuit Breakers Go Bad?
Anything can break in life, but in general, circuit breakers are reusable. But, yes, circuit breakers go bad in some situations, like most products after years of wear and tear.
After an outage, you can flip the circuit breaker switch back on without having to go out and replace it. Bad fuses, on the other hand, need to get replaced. After a fuse gets blown, you’ll have to get it replaced.
Types of Circuit Breakers
How do you know what type of circuit breaker to buy?
As a reminder, circuit breakers exist to protect your home from electrical hazards. A circuit breaker will disconnect power when it detects a current that exceeds its amperage. So consequently, by getting the wrong-sized circuit breaker, you could cause a fire. So the first step that a licensed electrician will do is evaluate the electrical load capacity. As an example, most household circuits are rated either 15 amps or 20 amps.
According to HomElectrical: “Every circuit breaker has a specified amperage (amount of current). This rating is labeled on the circuit breaker itself. The standard for most household circuits is rated as either 15 amps or 20 amps. An important note to remember is that circuit breakers can only handle about 80% of their overall amperage. That means a 15-amp circuit breaker can handle around 12-amps, and a 20-amp circuit breaker can handle about 16 amps.”
Next, determine the number of electrical devices a circuit breaker can handle. You do this by checking the wattage on the back of whatever device you’re powering. Also, “measure the voltage on the circuit you wish to install your electrical devices. Most household circuits are 120V, and larger commercial spaces are 240V”. For more information on this subject, visit HomElectrical’s detailed explanation.
The 5 Most Popular Circuit Breakers
- Eaton Circuit Breakers
- Square D Circuit Breakers
- Cutler-Hammer Circuit Breakers
- Siemens Circuit Breakers
- GE Circuit Breakers
What types of fuses are there?
There are many different types of fuses used to protect individual 120-volt circuits from larger 240-volt circuits.
For example, Edison Base Type (T) fuses are designed to handle 125 volts or less and have an ampere rating of no more than 30 amps. This is the standard fuse for most 120/125-volt household circuits.
There are also Type S and Cartridge fuses. “Cartridge fuses are used not only for 240-volt appliance circuits but also for the ‘main fuse’ that controls power to the entire fuse panel. Like screw-in fuses, cartridge fuses also have amperage ratings printed on them. The main fuses are often 60-amp, while fuses for appliance circuits are more typically 30-amp or 40-amp devices.”
Fuses are not reusable. Circuit breakers turn on and off, so they are reusable.
After a fuse burns, you’ll have to replace it, which is a downside to using a fuse box versus a circuit breaker.
How do you know if a fuse blows?
You’ll usually have a power outage when a fuse blows. Unfortunately, you can’t just go down to your basement and switch back on the circuit, as you would do with a circuit breaker system. With fuses, you have to replace blown fuses. To confirm you’ve blown a fuse, open up your panel and look inside the small glass window of the fuse.
On the outside of a fuse is a tiny glass window. You can see the strip of metal inside a fuse by looking through this glass. For example, after a fuse blows, you’ll see a cloudy-looking glass on the outside, indicating the fuse blew. If you then look inside the glass window on a blown fuse, you’ll see the melted metal strip inside the window. That melted strip is how you can verify a blown fuse.
How to replace a blown fuse
Replacing a fuse is easy; you unscrew the old one and screw in the new one.
Should I replace a blown fuse on my own?
Get a consultation from a licensed electrician to help you diagnose the cause of the blown fuse to ensure the underlying issue isn’t a hazardous situation.
So often, consumers try diagnosing and replacing a blown fuse on their own. Only to continue having power outages and paying excessive dollars to continue troubleshooting the issue on their own.
Dangers of replacing a fuse after it blows on your own
In many situations, our residential clients at Integrity Electrical Services have tried to replace a fuse on their own and either get the wrong type of fuse or neglect to address an underlying issue that caused the fuse to blow.
And it can be dangerous to install a fuse that is larger than the one you are replacing. Buzz Electrical Services explains, “Using fuses with the wrong voltage for your box can allow too much electrical current to run through your wiring and cause a fire.”
How to tell if your home has a Fuse Box or Circuit Breaker?
To figure out if you have a circuit breaker or fuse box, look inside your electrical panel, which may be in the basement, laundry room, or garage. That’s where you’ll find out whether you have a fuse box or circuit breaker.
A fuse box contains a group of round screw-in plugs with small glass windows. Circuit breakers are inside your electrical panel box but appear as rectangular units that you can turn on and off, all organized in rows.
How does a short circuit occur?
According to Pacific, “A short circuit occurs when electricity strays from its intended path and completes its journey via a more straightforward route—one of less resistance. This happens when the flow of electricity is interrupted by a flaw in the established wiring. If a short circuit in your electrical system is not found and promptly fixed, it could produce sparks, smoke, or fire or cause electric shock. ”
Benefits of a Circuit Breaker over a Fuse Fox
- Circuit breakers can be tested with ease, not having to get replaced afterward. However, fuses need to be thrown out after testing and replaced. How much do fuses cost? Each fuse can cost around $5-$10. Replacements costs (including labor and downtime) can add up, making fuses a more expensive route than using a circuit breaker.
- Circuit breakers require less wiring.
- Circuit breakers offer ground fault protection, and a fuse does not.
- Circuit Breakers last longer and don’t have to be replaced every time after an overcurrent trip. With a circuit breaker, all you would need to do is flip the circuit back on, and your electricity gets restored—Fuses meltdown (or blow) and need to get replaced.
Benefits of a Fuse over a Circuit Breaker
- You have a variety of fuse types to choose from, which can benefit you at times.
- Fuses trip faster than a circuit breaker.
- Fuses don’t require as much maintenance as circuit breakers, also making them more reliable over time.
Should I replace my fuse box with a circuit panel?
You may want to replace your fuse box with a modernized circuit panel. However, before you swap the two-out, you’ll want to have a licensed electrician check out your entire home’s wiring and possibly consider upgrading your electrical panel to at least a 200 amp, or maybe higher. If you plan to get an electric vehicle, like a Tesla and want an EV charger installed, and you have a generator installed already, at least a 200-amp panel upgrade will be required.
Suppose your home’s electricity is running off a fuse box. In that case, there’s a good chance your electrical service needs to be updated because most modern homes require at least a 200 amp circuit breaker panel, as we mentioned in the beginning. Unfortunately, fuse panels only provide 30 or 60 amps of power. If you have an older home, though, and do not need modern-day technology, you may be just fine with your fuse box as it is. The choice is yours. Massachusetts residents should talk to a local electrician at Integrity Electrical Services for answers to questions at (978) 753-8350.
Who is Integrity Electrical Services?
Integrity Electrical Services is an A+ BBB-rated Wilmington, Massachusetts-based electrical company. In addition, If you have any questions regarding Circuit Breakers or Fuses, give one of our licensed electricians a call.
Sources:
C3controls, “Circuit Breaker or Fuse? What’s the difference?“, www.c3controls.com/white-paper/circuit-breaker-or-fuse-difference/
YouTube, How Fuses and Circuit Breakers Work, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gDBUqeqx5t4
Buzz Electrical Services, “Fuse Box vs. Circuit Breaker: What Is the Difference?”, https://buzzelectricalnwa.com/fuse-box-vs-circuit-breaker-what-is-the-difference/
Pacific, https://www.pacificsheetmetal.net/about-us
HomElectrical, How to Determine the Load Capacity of Your Circuit Breaker, https://www.homelectrical.com/understanding-capacity-your-circuit-breaker.6.html#load%20capacity
The Spruce, Understanding Fuses and Fuse Boxes, https://www.thespruce.com/fuses-and-fuse-boxes-101-4122558